Combating climate change is becoming a top priority for businesses worldwide as pressure mounts from stakeholders, including regulators, investors, and consumers.
Many decision makers are accelerating the development of environmental sustainability strategies, with supply chain sustainability – including the impact of printing – under scrutiny. A growing number of brands now expect their suppliers to show that they are reducing their environmental impact, with some implementing measures to formally track their suppliers’ environmental performance.
For packaging converters, demonstrating sustainable practices can be challenging, as packaging and label creation can consume a lot of energy and water while producing avoidable waste.
In this blog, we’ll highlight how modern digital printing technology can help converters to reduce the environmental impact of packaging and label creation, supporting their and their brand customers’ sustainability objectives.
The status quo
Flexographic printing, with a traditional ‘forecast demand’ business model, has long been the go-to packaging print option for consumer brands when dealing with established, high-volume SKUs. However, changing consumer demand often fuels the creation of new experimental products, including seasonal, and promotional releases. In such instances predicting packaging volumes can be difficult, with brands preferring to source smaller quantities of packaging to avoid waste while the product is unproven.
Responding to increasing demand for shorter print runs can be a challenge for flexo converters, as the creation of printing plates and time-consuming press set-up aren’t cost-effective, and can lead to excess waste, when printing small volumes.
Adding digital printing capability to flexo presses to create a hybrid line, or investing in a digital roll-to-roll press alongside established flexo lines could help converters to adopt a more sustainable ‘print-on-demand’ business model for shorter run packaging.
A digital business model for more sustainable printing practices
Digital printing technology, used in a roll-to-roll or as part of a hybrid printing process, enables converters to offer an entirely new business model to their brand customers, with the ability to deliver short-run or variable product packaging while cutting costs and reducing waste from the creation of excess stock.
Reducing avoidable print waste saves money for converters and brands and reduces the environmental impact of handling and recycling printed stock. Energy used in the transport and recycling processes for excess stock will contribute to a brand’s overall carbon emissions. In addition, large volumes of water and chemicals are often used to de-ink excess stock for recycling, with a risk of pollution if items are handled incorrectly.
Achieving printing waste reduction
In the packaging industry, print waste encompasses much more than just printed packaging that has to be discarded due to overstock and obsolescence. Digital printing technology offers several opportunities for converters to lower the environmental impact of their operation versus traditional printing processes, as well as ways to improve the environmental performance of flexo processes as part of a digital hybrid process:
- The pricing model for digital printing means converters need only produce the number of units required, unlocking the potential to transition to a print-on-demand packaging model.
With print on demand, excess stock is effectively eliminated, saving energy, reducing ink and substrate use, and lowering the need for transporting and recycling excess stock.
- Digital printing technology can also facilitate waste-reducing packaging customisation opportunities, including late-stage customisation.
With late-stage customisation, finishing touches are added to pre-printed stock at the manufacturer’s facility, typically via monochrome print. The packaging design is printed in bulk by a converter, and details requiring frequent updates, such as promotional content or variable data, are only added shortly before or during the packaging process, helping to reduce obsolescence.
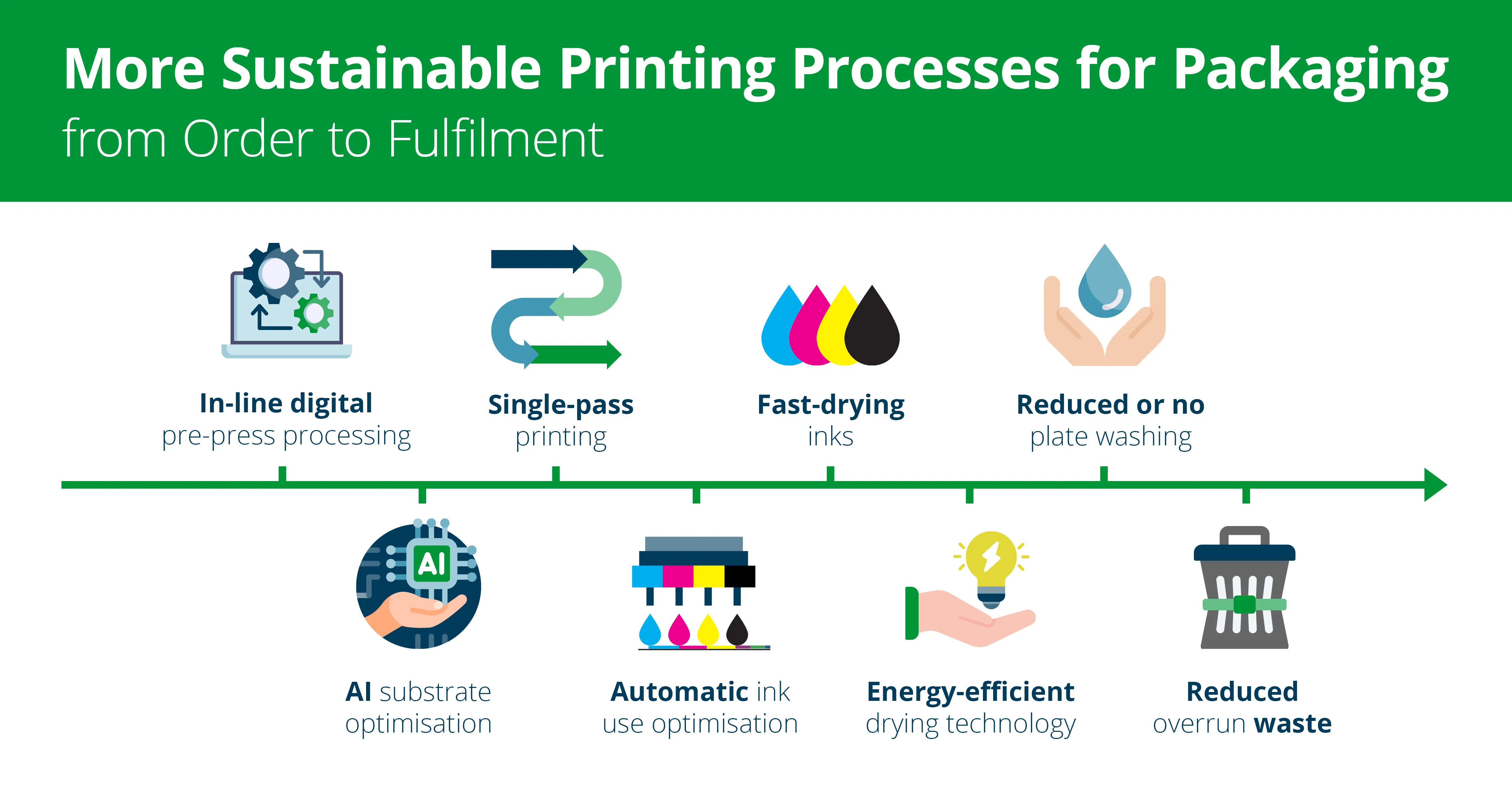
- Digital printing doesn’t require the use of printing plates – one of the most significant sources of waste in analogue printing processes. Those opting for a full-, or hybrid-digital process over analogue can greatly reduce lead times and avoid, or significantly reduce plate-related waste.
Plates and analogue pre-press waste – such as ink and media used during setup and proofing – can account for more than 10% of a brand’s annual spending, depending on the number of SKUs and variations produced[1]. By comparison, reducing or eliminating use of plates helps reduce water consumption, ink waste, and chemical waste during plate cleaning, as well as the need for treating contaminated wastewater.
- Converters using digital print technology for short-run packaging can also expect efficiency gains when it comes to consumables and energy use. Enabled by the precise drop placement of digital inkjet printheads, digital inkjet presses only use the amount of ink needed to create the label design, without residual ink on analogue plates going to waste at job changeover.
Onboard automation of maintenance tasks, such as printhead cleaning and constant ink circulation, can help ensure reliable, efficient performance while reducing overall consumables use.
In addition, the high-efficiency drying technology featured in modern digital inkjet label and corrugated presses typically uses fewer pinning and curing lamps versus flexo processes, where lamp(s) are often included after each flexo station. This, in turn, can deliver energy savings.
The overall reduction in consumables and energy use during press usage can contribute to a reduction in carbon emissions across the supply chain – as well as offer cost savings.

Sustainable printing practices: automation and AI
Software, AI, and automation are playing an increasingly significant role in optimising production workflows to support more sustainable printing practices for digital, hybrid, and analogue processes.
In digital printing, automating the pre-press workflow via digital front-end software enables digital proofing, saving time and eliminating the need for, and additional waste from, hard proofs. Real-time inline RIP (raster image processing) capabilities onboard digital presses help to maximise press utilisation, which in turn can help to reduce energy use while idle and lower the environmental impact per print.
Machine vision technology can help enhance both digital and analogue printing processes, as detecting issues that impact print quality as soon as they arise allows for quick intervention to correct the issue, helping to minimise print rejects and press downtime.
Hardware automation also has a role to play. Combining pre-press, printing, and finishing in a single, automated hybrid label printing process can help to reduce power consumption as set-up times are shorter and job changeovers are more efficient[2]. Continuous processes typically also use less material, as waste from overrun in each process step is eliminated, benefiting both the environment and the converter’s bottom line.
In addition, interest in AI tools to enhance print performance is growing. Automatic monitoring and enhancement of production patterns can help converters save time, improve print operation efficiency, reduce downtime, and minimise print waste – contributing to a lower sustainability footprint for the overall operation[3].
Digital printing: making your printing operation more sustainable
In the right scenario, digital printing technology can help converters and their brand customers establish more sustainable consumption and production patterns in line with wider sustainability commitments and offers significant opportunities for cutting avoidable waste – including print-on-demand business models and late-stage customisation.
Those switching to digital or upgrading analogue printing processes with a digital printing module for their short to medium runs can expect to reduce waste and associated carbon emissions, while increasing overall efficiency, making cost savings that positively impact profitability – a win-win situation!
Converters looking to invest in digital printing technology to support their transition to more sustainable printing practices should work with a digital printing equipment supplier who continually invests in making printing processes more efficient, optimising energy use, and reducing print waste.
Find out more about Domino’s digital printing solutions here.
References:
[1] Keypoint Intelligence, State of the Industry: Global Intelligence for Corrugated Packaging, November 2023.
[2] Smithers, The Future of Printed Labels to 2029, 2024.
[3] Smithers, The Future of Printed Labels to 2029, 2024.